Alzheimer’s disease – Symptoms, Risks, symptoms and stages, elderly disease, dementia, memory loss
Alzheimer’s disease is a progressive neurodegenerative disorder. Alzheimer disease involves deterioration of brain cells and causes memory loss, affecting thinking and cognitive decline. This disease is one of biggest factor for causing dementia in older adults. The exact cause of Alzheimer’s disease is not yet known, but it is believed to be caused by a combination of genetic, environmental, and lifestyle factors. There is no cure for Alzheimer’s disease, but there are treatments that can help to slow the progression of the disease, and manage symptoms.
What is risk at present in Human to get Alzheimer’s disease in another 10-20 years?
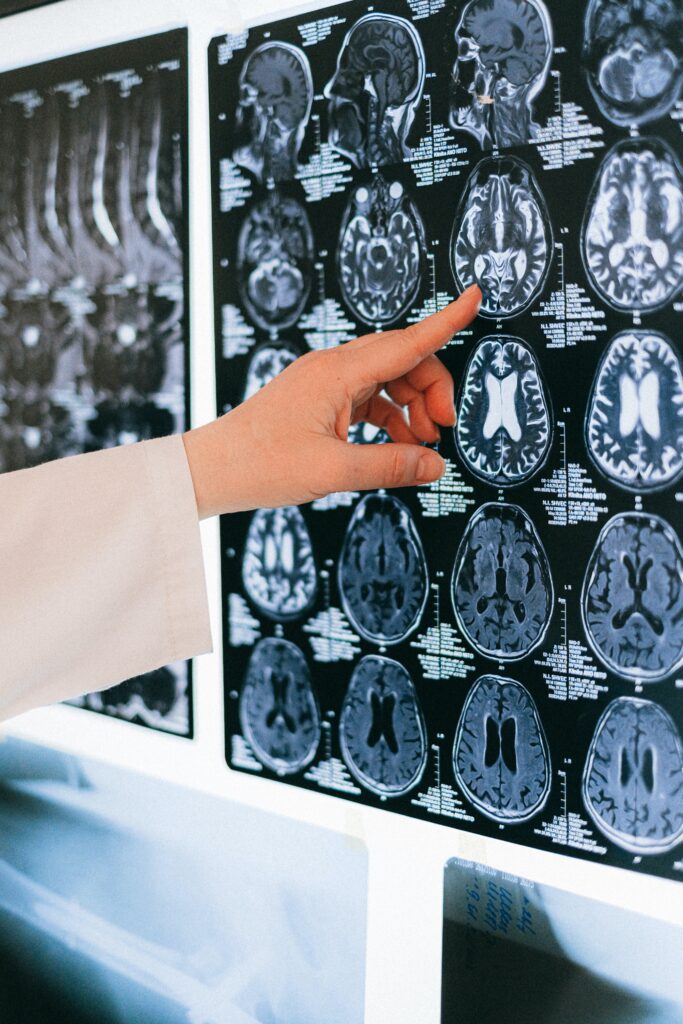
The risk of developing Alzheimer’s disease increases with age, and it is estimated that around 3% of people over the age of 65 have the disease.
It is estimated that the number of people with Alzheimer’s disease worldwide will triple to 152 million by 2050, due to the aging population and the increasing prevalence of risk factors such as diabetes and obesity.
Symptoms:
The symptoms of disease can vary from person to person, but they generally include:
- Memory loss that disturbs daily life
- Difficulty in completing familiar tasks
- Confusion with time or place
- Difficulty in planning or solving problems
- Problems in understanding visual images and spatial relationships
- Confusion and lack of coordination with words in speaking or writing
- Misplacing things
- Losing the ability to retrace steps, paths to home, or common task steps
- Decreased or poor judgment
- Withdrawal from work or social activities
- Frequent changes in mood
- Changes in personality and confidence or sometimes overconfidence.
- Rigidness in Behaviour
Diagnosis
Alzheimer disease treatment required a thorough medical evaluation of a person.
This includes a physical exam, neurological exam, and cognitive tests. The doctor may also order brain imaging tests such as MRI or CT scans to rule out other conditions that may cause similar symptoms. There is no single test that can diagnose Alzheimer’s disease, but the combination of these tests can help doctors make an accurate diagnosis.
It is important to note that early diagnosis of Alzheimer’s disease can help people with the disease and their families plan for the future and receive appropriate treatment. We many times ignore our near Ones health conditions. With increasing age sometimes we think it is behavior changes due to age. Be Cautious, if you or someone you know is experiencing any of the symptoms of Alzheimer’s disease, it is important to consult a doctor for an accurate diagnosis and treatment options.
Alzheimer’s disease and progression
This disease is a progressive disorder that affects the brain and causes memory loss, thinking problems, and behavioral changes. The disease progresses slowly over time and can be divided into three stages: mild, moderate, and severe.
The mild stage of Alzheimer’s disease is characterized by memory loss, difficulty in performing familiar tasks, and problems with language. People in this stage may also experience mood swings, personality changes, and difficulty in making decisions.
In the moderate stage, the symptoms of Alzheimer’s disease become more pronounced. People in this stage may have difficulty recognizing family members and friends, experience confusion about where they are or what day it is, and have trouble with basic tasks such as dressing themselves. They may also experience hallucinations or delusions.
The severe stage of Alzheimer’s disease is characterized by a significant decline in cognitive function. People in this stage may lose the ability to communicate or respond to their environment, require assistance with daily activities such as eating and using the restroom, and may experience seizures or other medical complications.
It is important to note that not everyone with Alzheimer’s disease will experience all of these symptoms, and the progression of the disease can vary from person to person.
Life expectancy of a person with Alzheimer’s disease
According to the Alzheimer’s Association, people with Alzheimer’s disease live an average of four to eight years after diagnosis, but some people can live up to 20 years with the disease. It is important to note that these are just estimates and not everyone with Alzheimer’s disease will experience the same progression or symptoms. The life expectancy of a person with Alzheimer’s disease can vary depending on the stage of the disease and other factors such as age, overall health, and the presence of other medical conditions.
Treatments:
There is no exact cure for Alzheimer’s disease, but it can be managed and the quality of life for people with the disease can be improved. Some of the treatments include:
· Medications: Alzheimer disease medication can help manage the symptoms of Alzheimer’s disease. Donepezil, galantamine, and rivastigmine can be prescribed for people with early- to mid-stage of disease. These medications work by regulating neurotransmitters in the brain and can help improve memory, thinking, and behavior. Consult a medical practitioner for the right dosage and treatment.
· Therapies: Different therapies like occupational therapy, speech therapy, and cognitive therapy can help people with Alzheimer’s disease. Occupational therapy can increase cognitive health and mental well-being. To manage daily routines and activities it can be especially beneficial for patients.
Speech therapist professional offers help in language, communication, information processing, memory improvement, as well as eating, drinking, and swallowing guidelines.
While, Cognitive therapy is helpful when tailored to an individual approach. Cognitive rehabilitation prepares a framework and strategies to attain improvement in movements, maintain day-to-day activities, and prevent falls or injuries.
· Lifestyle changes: Making certain lifestyle changes is necessary to decrease this progressive disease. These changes include regular exercise, a healthy diet, Yoga, scheduled walks, and more importantly social engagement. Staying with family, friends, clubs, or any social group provides a significant delay in disease progression. Keep happy and engaged.
How can I reduce my risk of developing Alzheimer’s disease?

There are some activities that help to prevent risk up to some extent, here are below:
- Exercise regularly: Minimum 30 mins daily or 3 sessions of activities like cycling, running, swimming, or any outdoor play is recommended. This not only keeps you physically fit but improves blood flow to the brain and reduces the risk of developing Alzheimer’s disease. Lifestyle needs to be active when you are in your 30s. It is never too late, so start from where you are.
- Eat a healthy diet: A daily serving of fresh fruits, vegetables, and whole grains can help reduce the risk of developing Alzheimer’s disease.
- Stay mentally active: When we learn new skills we make new Neurons paths. Engaging in mentally stimulating activities such as reading, playing games, or learning a new skill can help reduce the risk of developing Alzheimer’s disease. Learning a new language can help a lot to make the brain active and set up new learning paths. Learning a new language can keep your brain sharp even at elderly age.
- Stay socially active: Humans are social animals. In wartime or prisons, the hardest punishment is to keep a person in isolated cells. During COVID-19 in 2019-2021, the World has seen how difficult to stay in Lockdown. Maintaining social connections with friends and family can help reduce the risk of developing Alzheimer’s disease. Meet your friends, family, and interest clubs regularly. Travel or do a social activity together. Volunteering is another good option.
- Manage chronic conditions: Chronic conditions such as high blood pressure, diabetes, and high cholesterol can increase the risk of developing Alzheimer’s disease. Managing these conditions can help reduce the risk. If you suffering from any, take medication on time. Revisit your diet and lifestyle as healthy as possible.
It is important to note that while these tips may help reduce the risk of developing Alzheimer’s disease, they are not a guarantee. Keep yourself with a Positive Mind-set. Stay active and nourish your body with nutritious food.
Stay Positive and Happy!!
